FLAT1 (Flathead, MT, Lat. 48, Long. -114.7)
Based on the data available from 6/2002-12/2003, organics emitted from regional forest fires is the major cause of haze at the Flathead.
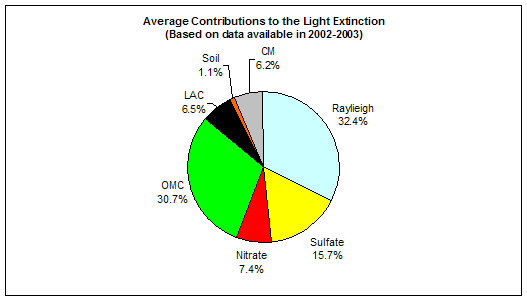
In Flathead, the average PM2.5 mass concentration during 6/2002-12/2003 is 4.1 mg/m3, and the average total light extinction coefficient (Bext) is 31 Mm-1 (Visual Range ~ 126 Km; Deciview ~ 11). OMC is the largest contributor to haze, with an average contribution of ~ 31%.

Figure 1. Average contributions of major aerosol chemical components to light extinction
Based on the data in 2003, the average light extinctions in the 20% best, middle 60% and 20% worst haze days are calculated and shown in Figure 2. The light extinction coefficient of 67 Mm-1 in the 20% worst days is about 2.8 and 4.5 times of the values in the middle 60% and 20% best days. Organics is the largest contributor to haze in the 20% worst days in 2003, with an average contribution of ~52%. Figure 3 suggests that, in 2003, the highest occurrence of the 20% worst days happened in August, in which ~80% of the sampling days are the 20% haziest days at Flathead. OMC, which is most likely from forest fires, contributes in average ~66% to light extinction in the 20% worst days during August 2003.
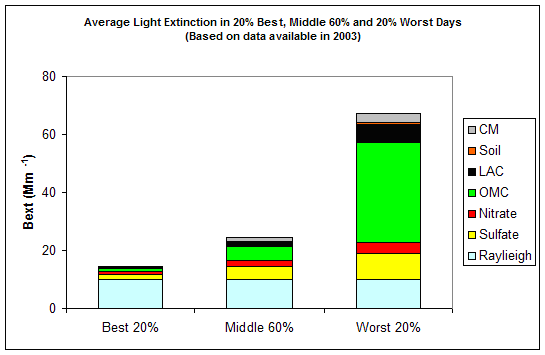
Figure 2 Average contributions of major aerosol chemical components to light extinction in 20% best, middle 60% and 20% worst days
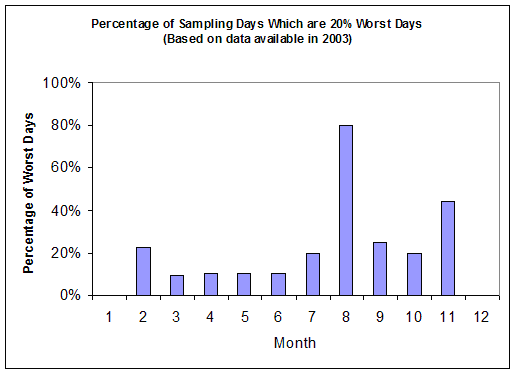
Figure 3 Percentage of sampling days that are 20% worst days in each month
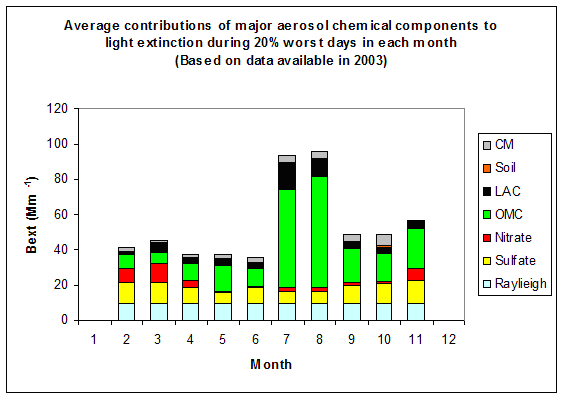
Figure 4 Average contributions of major aerosol chemical components to light extinction during 20% worst days in each month