Cluster Analysis
Description of Cluster Analysis
Cluster analysis is a data analysis tool for solving classification
problems. Its object is to sort cases into groups, or clusters, so that the
degree of association is strong between members of the same cluster and weak
between members of different clusters. Group members will share certain
properties in common and it is hoped that the resultant classification will
provide some insight into our research topic. The general categories of cluster
analysis methods include Joining (Tree Clustering), Two-way Joining, K-means
Clustering, et al. A detailed description of the cluster analysis can be found
at
http://www.statsoftinc.com/textbook/stcluan.html.
In this study, cluster analysis is used to identify similar and dissimilar
aerosol monitoring sites so that we can test the ability of the Causes of Haze
Assessment methods to explain the similarities and differences. The major
clustering algorithm used in this study is joining or tree clustering.
Joining (Tree Clustering)
The purpose of this algorithm is to join together objects into successively
larger clusters, using some measure of
similarity or distance. A typical result of this type of clustering is a
hierarchical tree as shown below.
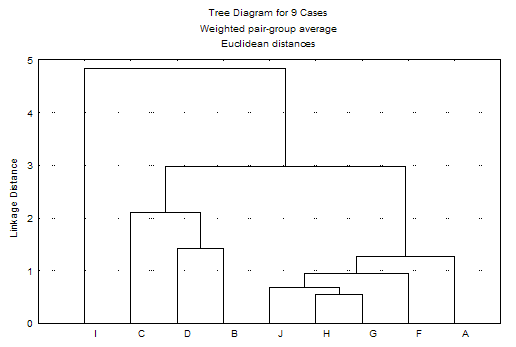
At the beginning, each object is in a class by itself. Then, we lower our
threshold regarding the decision when to declare two or more objects to be
members of the same cluster. As a result more and more objects are linked
together following certain Amalgamation or
linkage rules and aggregate larger and larger clusters of increasingly
dissimilar elements. Finally, in the last step, all objects are joined together.
In the plot, the vertical axis denotes the linkage distance. Thus the higher the
level of aggregation, the less similar are the members in the respective class.
